
Lens - Changes shape to help focus on images on the retina.Irus - Colour of the eye surrounds the pupil and is the muscle that expands and contracts to change the size of the pupil for light.Bathroom in the dark: You don't need to turn the lights on in the middle of the night because you're guided by your expectations in the bathroom.Perception constructed by cognition Example


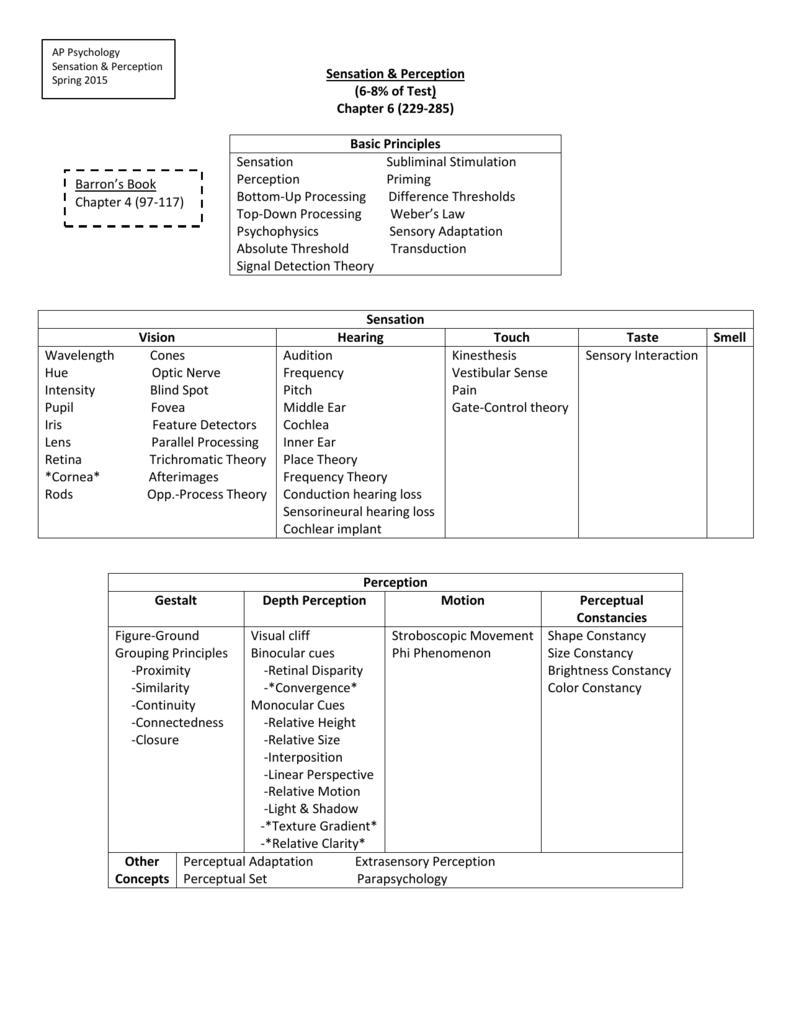
When you see a mosquito, you see a mosquito and then interprets the sensor receptor's info.Anagram - Starting with individual pieces (letters) and works up to make bigger pieces (words).īottom-Up Processing Īnalysis that begins with sensory receptors and works up to the brain's integration of sensory info. Weber's Law - Two stimuli must differ by a constant minimum percentage (rather than a constant amount), to be perceived as different.Difference Threshold - Minimum difference between 2 stimuli required for detention 50% of the time (just noticeable difference ).Intensity - Great amplitude (bright, loud)/Small amplitude (dull, soft).Long wavelength - Low frequency (red, low pitched) = Clifford.Short wavelength - High frequency (blue, high-pitched) = Smurf.Phototransduction - Light energy -> neural impulses the brain can understand.Microsaccades - Constant movement of the eyes (tiny vibrations) that you don't understand.Habituation - Tendency of the brain to stop attending to constant, unchanging info.Sensory Adaptation - Diminished sensitivity as a consequence of constant stimulation (put a band-aid on your arm for a while then you won't realize it is there).Subliminal Threshold - When stimuli are below one's absolute threshold for conscious awareness (not enough to be consciously aware of something).Signal Detection Theory - Theory predicting how and when we detect the presence of a faint stimulus (signal) amid background stimulus (noise).Example: Vision - A single candle flame from 30 miles on a dark, clear night Hearing - Hear a watch's tick in a quiet environment at 20 feet. Absolute Threshold (Gustav Fechner) - Minimum stimulation needed to detect a particular stimulus 50% of the time.Psychophysics - Study of the relationship between physical characteristics of stimuli and our psychological experience with them.Transform (stimulation -> neural impulses).There are 3 steps every time you convert sensory energy to get the info to your brain. Transduction - Conversion of one form of energy to another form.Perception - Process of organizing and interpreting sensory info.Sensation - How we detect physical energy from the environment and encode it as neural signals.The mechanisms of the 5 senses and sensory disorders.The role of experience and culture in perception.Basic principles of how humans experience and process stimuli.Introduces how humans perceive and process the world around them via their senses and convert those observations into perceptions that influence how we think and behave.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
